 Community dynamics may play a role in population cycles.
Community dynamics may play a role in population cycles.
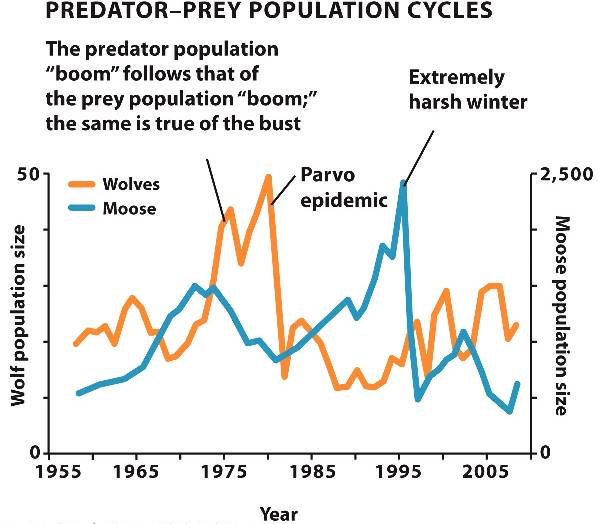
This example from Isle Royale in Michigan illustrates the inter-dependent nature of a predator-prey relationship.
The boom and bust cycles of the predator (wolves) often follow those of the prey (moose) population; other factors such as virus outbreaks and severe weather also play a role: the Parvo epidemic of the early 1980's caused the wolf population to crash.